Python3.11正式版,它来了!

Python3.11正式版,它来了!
蔡坨坨转载请注明出处❤️
作者:测试蔡坨坨
原文链接:caituotuo.top/b055fbf2.html
你好,我是测试蔡坨坨。
就在前几天,2022年10月24日,Python3.11正式版发布了!

Python官方在2020年1月1日结束了对Python2的维护,这也意味着Python2已经成为历史,真正进入了Python3时代。自从进入Python3版本以来,官方已经发布了众多修改版本分支,现在最新的正式版本就是前不久刚发布的Python3.11,这一版本历经17个月的开发,现在公开可用,据说对用户更友好。
今天,我们就来一起看看Python3.11都更新了些什么呢。
官方文档:https://docs.python.org/3.11/whatsnew/3.11.html
1 | # author: 测试蔡坨坨 |
速度更快
首先第一点,也是最重要的,就是它更快了,官方说法是Python 3.11比Python 3.10快10-60%。
Python 3.11 is between 10-60% faster than Python 3.10. On average, we measured a 1.25x speedup on the standard benchmark suite. See Faster CPython for details.
众所周知,Python语法简洁、功能强大,特别容易上手,因此使用人数超级多,在众多最受欢迎编程语言榜单中多次位列第一,但是它有一个明显的劣势就是纯Python编写的程序执行效率低,很多开发者都期待这门语言的性能有所提升。
更加人性化的报错
PEP 657: Fine-grained error locations in tracebacks
官方文档:https://docs.python.org/3.11/whatsnew/3.11.html#whatsnew311-pep657
When printing tracebacks, the interpreter will now point to the exact expression that caused the error, instead of just the line.
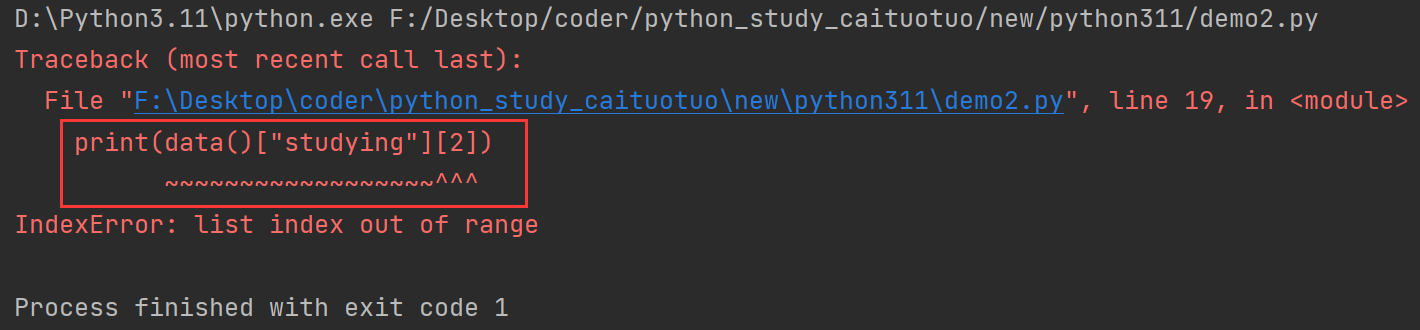
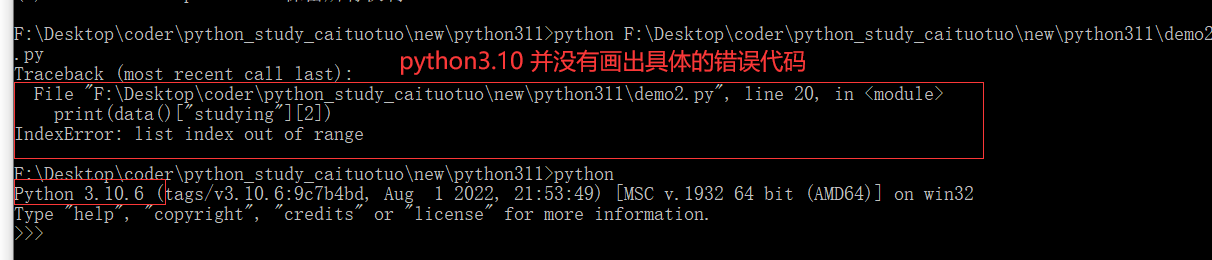
更加人性化的报错,与之前显示在某一行的报错不同,这个版本的报错会显示具体原因,画出具体位置。
Python编程语言对初学者非常友好,具有易于理解的语法和强大的数据结构,但是对于刚刚接触Python的同学来说却存在一个难题,即如何解释当Python遇到错误时显示的Traceback,有了这个功能就可以帮助用户快速解释错误消息。
举栗:
1 | # author: 测试蔡坨坨 |
一个IndexError的例子,我们可以看到嵌入在Traceback中的~和^符号详细地指向导致错误的代码,这种带注释的Traceback对于过于复杂的代码来说是比较友好的。
异常组
PEP 654: Exception Groups and except
官方文档:https://docs.python.org/3.11/whatsnew/3.11.html#whatsnew311-pep654
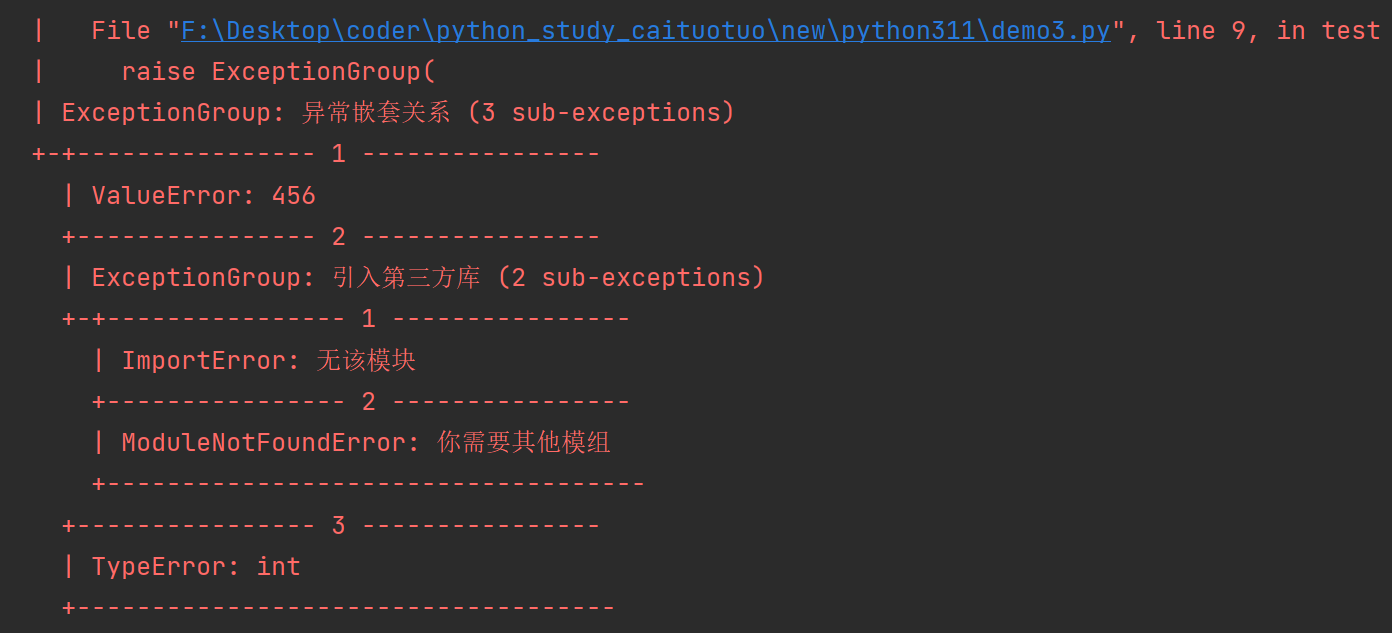
Exception Groups 让我们的Exception信息具有层次感,之前的Python每次只能处理一个Exception,异常组的使用丰富了Exception的作用,可以引入多个Exception,同时也丰富了我们代码分析的信息量。
举栗:
1 | # author: 测试蔡坨坨 |
支持TOML配置解析
PEP 680: tomllib — Support for parsing TOML in the Standard Library
官方文档:https://docs.python.org/3/library/tomllib.html#module-tomllib
增加了TOML(Tom’s Obvious Minimal Language 的缩写)文件的读取,toml文件与自动化测试框架或Web开发中的config、yaml文件类似,都是通过修改配置文件来保持框架源码的不变。Python社区已将TOML作为首选格式,虽然TOML已被使用多年,但Python并没有内置的TOML支持,而在Python3.11中tomllib已经是个内置模块,这个新模块建立在 toml 第三方库之上,允许解析 TOML 文件。
举栗:
demo.toml:
1 | # This is a TOML document. |
1 | # author: 测试蔡坨坨 |
更加安全
PEP 675: Arbitrary literal string type
官方文档:https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html#typing.LiteralString
The new LiteralString annotation may be used to indicate that a function parameter can be of any literal string type. This allows a function to accept arbitrary literal string types, as well as strings created from other literal strings. Type checkers can then enforce that sensitive functions, such as those that execute SQL statements or shell commands, are called only with static arguments, providing protection against injection attacks.
防止SQL注入,指定参数为LiteralString,当传入普通的String时就不可以工作。
1 | # author: 测试蔡坨坨 |
异常Notes
PEP 678: Exceptions can be enriched with notes
官方文档:https://docs.python.org/3/whatsnew/3.11.html#whatsnew311-pep678
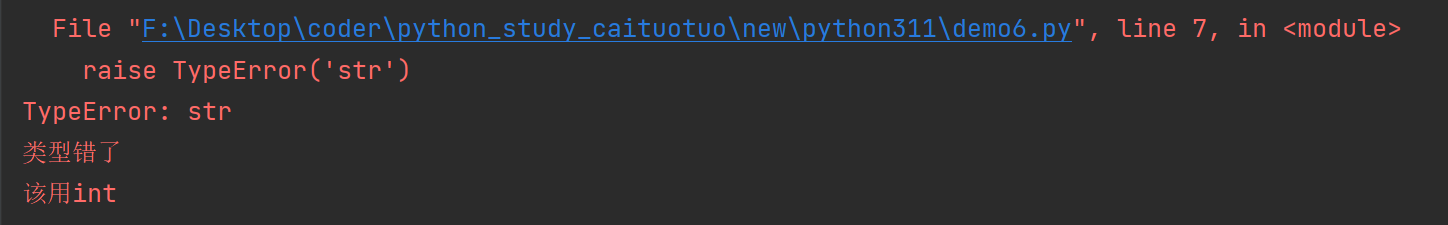
常规异常具有添加任意 notes 的扩展能力,可以使用.add_note()向任何异常添加一个note,并通过检查.__notes__属性来查看现有notes。
1 | # author: 测试蔡坨坨 |
以上几点就是我认为 Python 3.11 比较有意思的部分,更多内容可参考官方文档,想体验新功能的小伙伴感觉去试试新版本吧 ~